What Are the Unique Properties Of Stainless Steel For Forging?
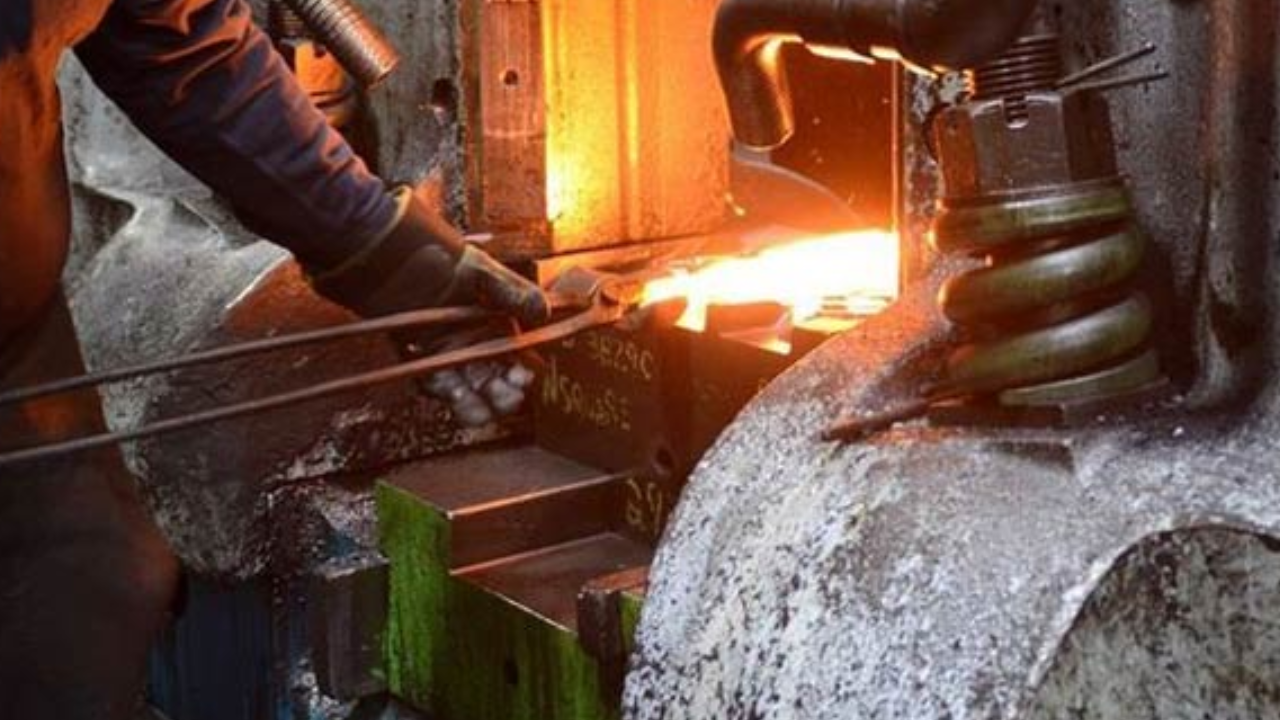

Stainless steel forging is a specialized metal forming process that converts raw stainless steel material into components with excellent strength and corrosion resistance. The procedure entails heating stainless steel to high temperatures before shaping it with dies and punches to achieve precise geometries.
It enables the manufacture of delicate and complex components with close tolerances and high precision. The forged stainless steel pieces that result have outstanding endurance, making them appropriate for essential applications requiring strength and corrosion resistance.
Quality control is essential in stainless steel forging, and it includes a comprehensive inspection of raw materials. The following link, https://www.cxinforging.com/stainless-steel-forged-component-products/ has detailed information regarding the stainless steel forgiving. Overall, stainless steel forging is a versatile and efficient technique that contributes to the creation of high-performance components for a wide range of industries.
Unique Properties of Stainless Steel For Forging
Stainless steel is a strong material in the field of forging, appreciated for its outstanding characteristics. When applied to stainless steel, the method of shaping metals by localized compressive stresses takes on new dimensions, unlocking a spectrum of unique properties that make it a popular choice across numerous industries. This article contains in-depth information regarding the properties of stainless steel.
Corrosion Resistance: The Pinnacle Feature
Corrosion resistance distinguishes stainless steel from other materials in forging applications. This resistance is related to the presence of chromium in the alloy, which forms a protective oxide layer on the surface. This oxide layer functions as a shield, preventing rust, discoloration, and corrosion even in harsh settings. The significance of corrosion resistance in forging cannot be overemphasized.
Exceptional Strength and Durability
The special features of stainless steel in forging include strength and durability. The forging process alone considerably improves the mechanical qualities of stainless steel. The grain structure of the material is refined during forging by applying localized compressive stresses, resulting in enhanced tensile strength, impact resistance, and fatigue strength.
Heat Resistance: Thriving In High-Temperature Environments
Certain kinds of stainless steel have high heat resistance, which increases their utility in forging applications. Components subjected to high temperatures, such as those found in industrial furnaces, and exhaust systems, and aerospace engines, benefit from the material's ability to retain structural integrity under thermal stress.
Versatility Unleashed: Forging Complex Shapes With Precision
The adaptability of stainless steel for forging is evidence of its adaptability to a wide range of manufacturing requirements. Because of the material's unusual combination of formability and strength, it can be forged into complicated forms and sizes. The forging versatility of stainless steel leads to the manufacture of components that not only meet functional requirements but also correspond to the stringent specifications of modern engineering.
Hygienic Properties: A Clean Slate for Medical and Food Applications
In addition to its mechanical strength, stainless steel has sanitary qualities that make it an excellent choice for medical and food applications. The non-porous, flat surface of stainless steel is easy to clean and inhibits the formation of microorganisms, making it ideal for these industries' rigorous hygiene standards. Medical and surgical equipment, allowing it to be sterilized and reused successfully.
Resistance to Wear and Abrasion
The resistance to wear and abrasion of stainless steel is a significant attribute in forging applications where components are subjected to friction, sliding, or abrasive environments. Certain stainless steel grades, particularly those with high hardness or certain alloying components, demonstrate outstanding wear resistance and surface integrity when subjected to abrasive forces.
Non-Magnetic Nature: A Magnetic Charm
The non-magnetic character of certain stainless steel grades is another distinguishing feature. While most stainless steels are nonmagnetic when annealed, some cold-worked or heat-treated circumstances can make them slightly magnetic. This feature provides another layer of versatility to stainless steel, making it suited for applications requiring minimal magnetic interference or attraction.
Ease of Fabrication and Machining
While forging is the primary method of producing stainless steel components, the material's ease of fabrication and machining is an added benefit. Secondary machining methods, such as milling, turning, or drilling, can be used on stainless steel forgings to produce tight tolerances or specialized geometries that may not be fully realized through forging alone.
Final Words
Stainless steel's unique forging qualities propel it into a league of its own in the world of materials engineering. Stainless steel is a material that flawlessly mixes design and function, thanks to its corrosion resistance, heat resistance, and adaptability. Stainless steel's enduring attractiveness in forging remains unwavering as sectors continue to innovate and require materials that push the boundaries of performance, determining the future of modern production.